The Redefinition of Agriculture Begins Here
Miravis Neo (Syngenta)
SKU 1072
$1,898.75
Bulk Discounts Available
Units in product: 5 gallons
Price per unit: $350 per gallon
Price incl. Sales Tax (8.5%) $148.75
Bulk pricing available for quantities of 5 units or more
Three modes of action for broad spectrum fungicide protection in corn, soybean, canola, quinoa and dry bean plants
Miravis Neo Volume
Please choose
In stock: 100 available
1
Buy more, save more
| Quantity | Price per item | Discount |
| 5 items | $1,790.24 | 6% off |
| 10 items | $1,708.86 | 10% off |
Product Details
Brand: Syngenta
Weight: 50.00 lbs
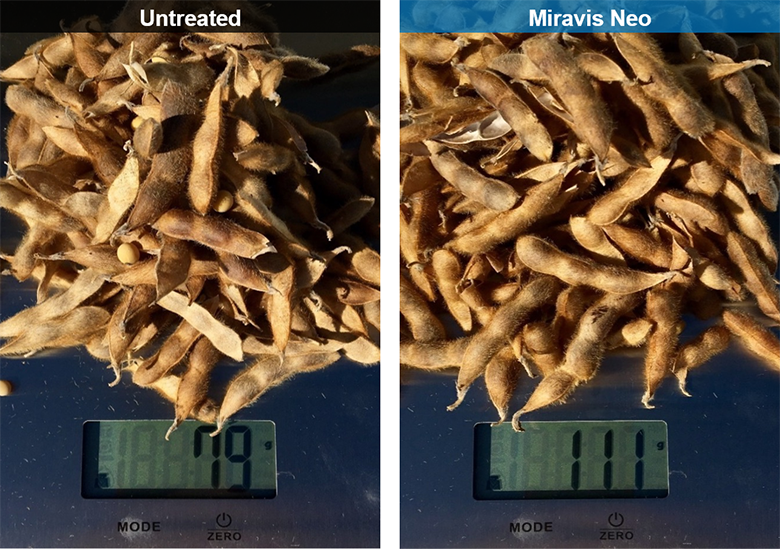
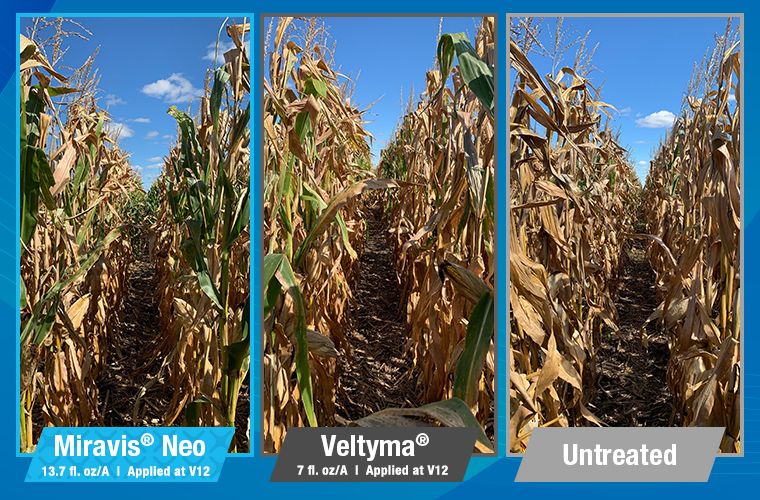
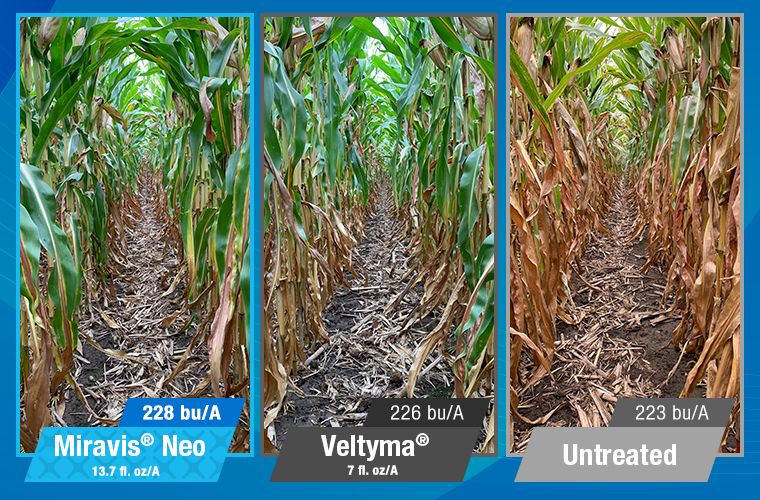
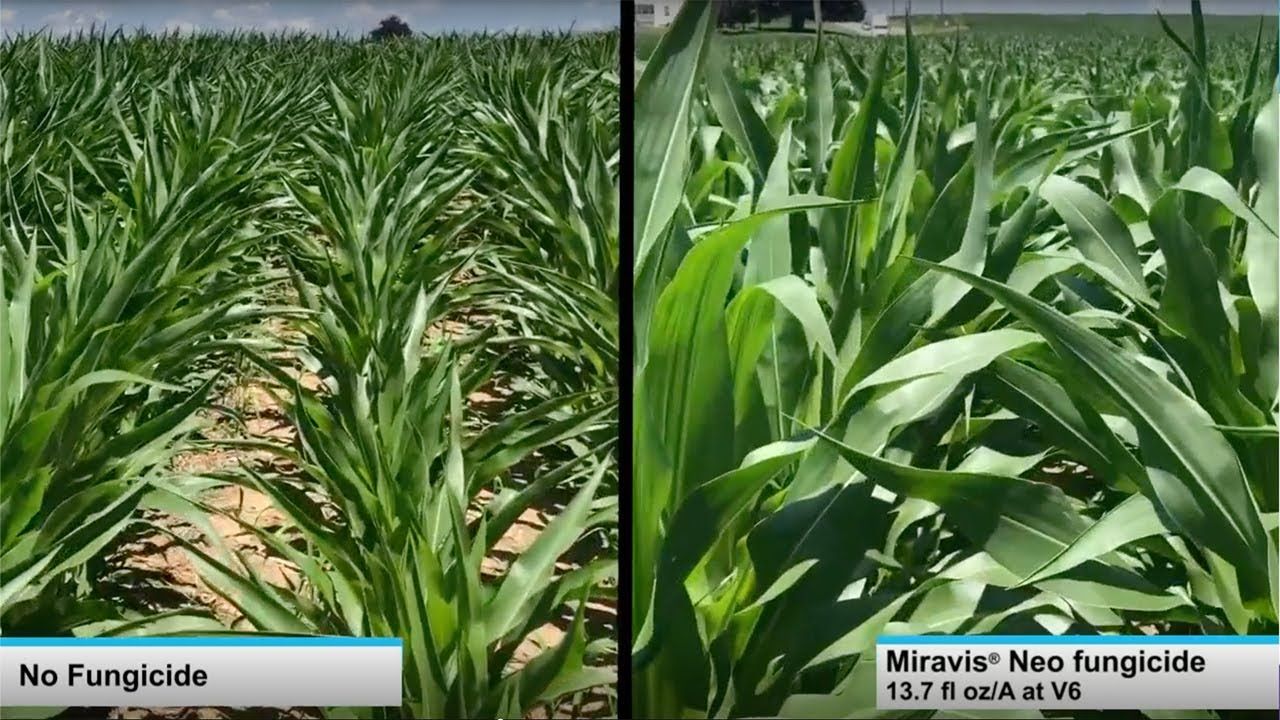
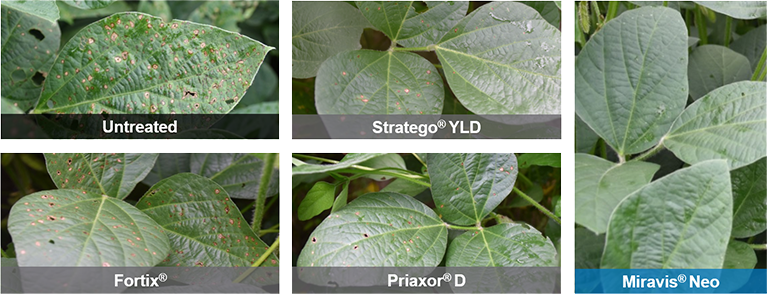
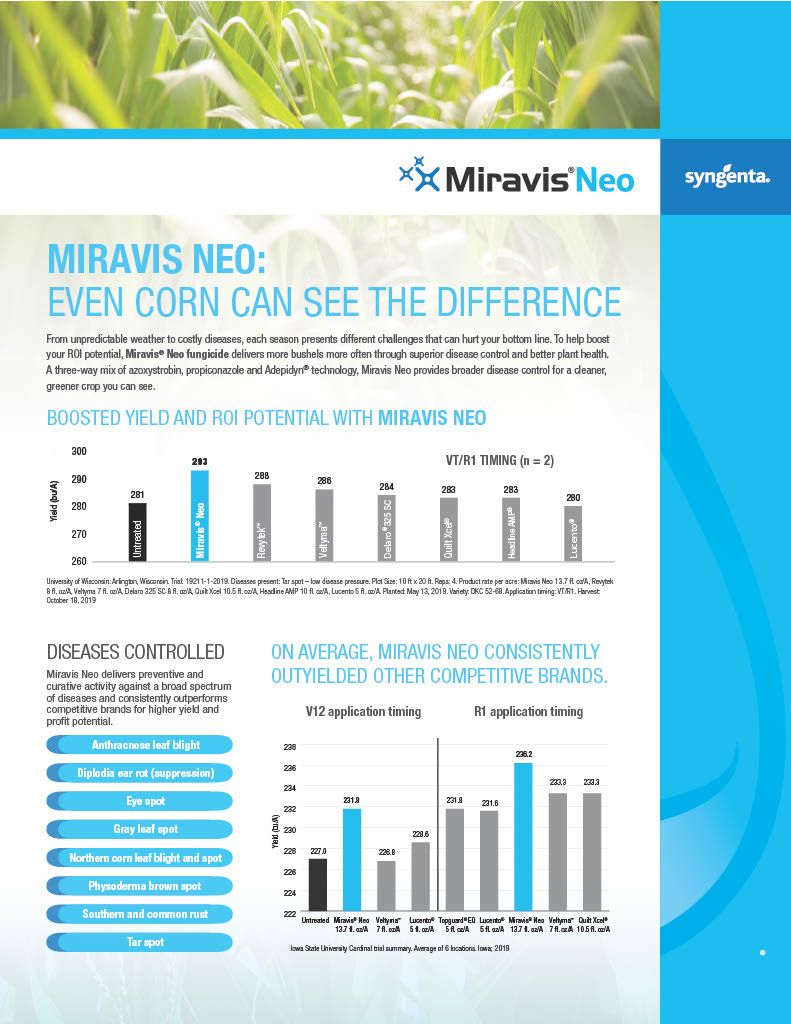
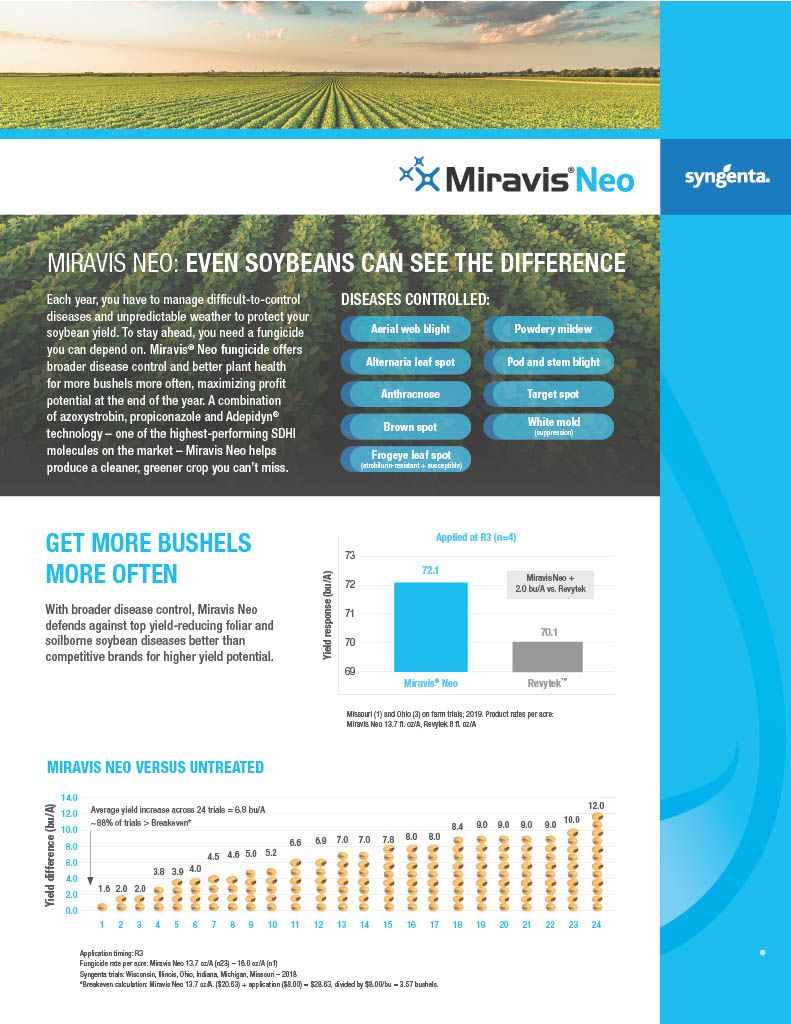
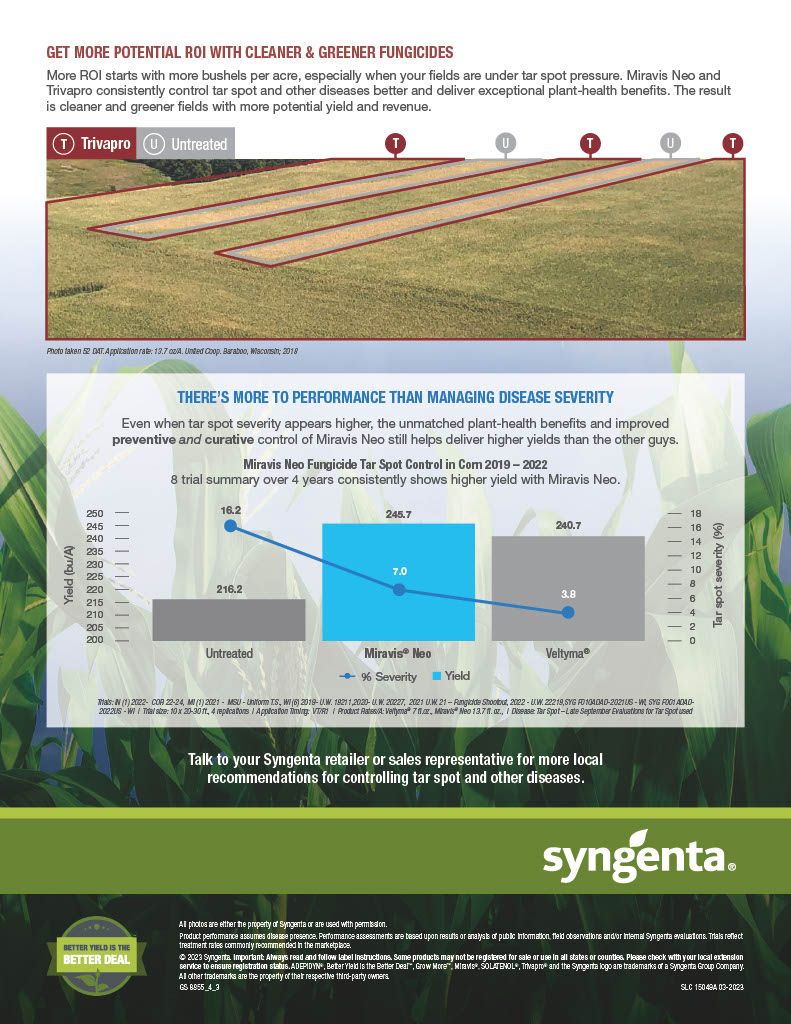
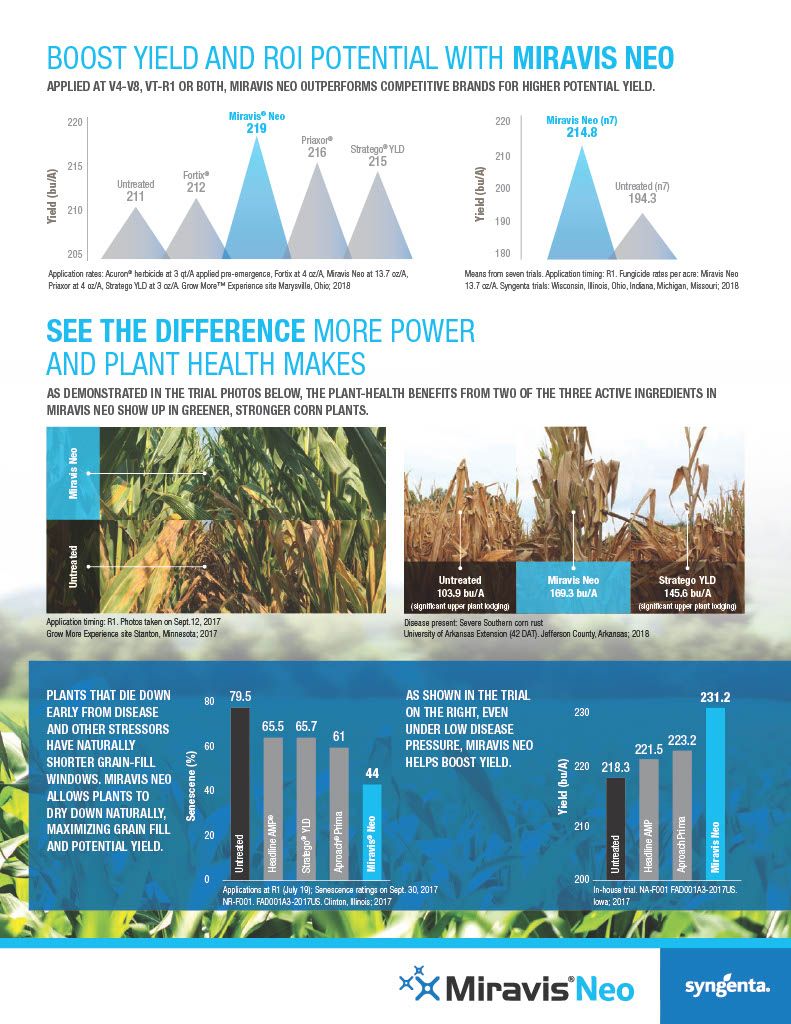
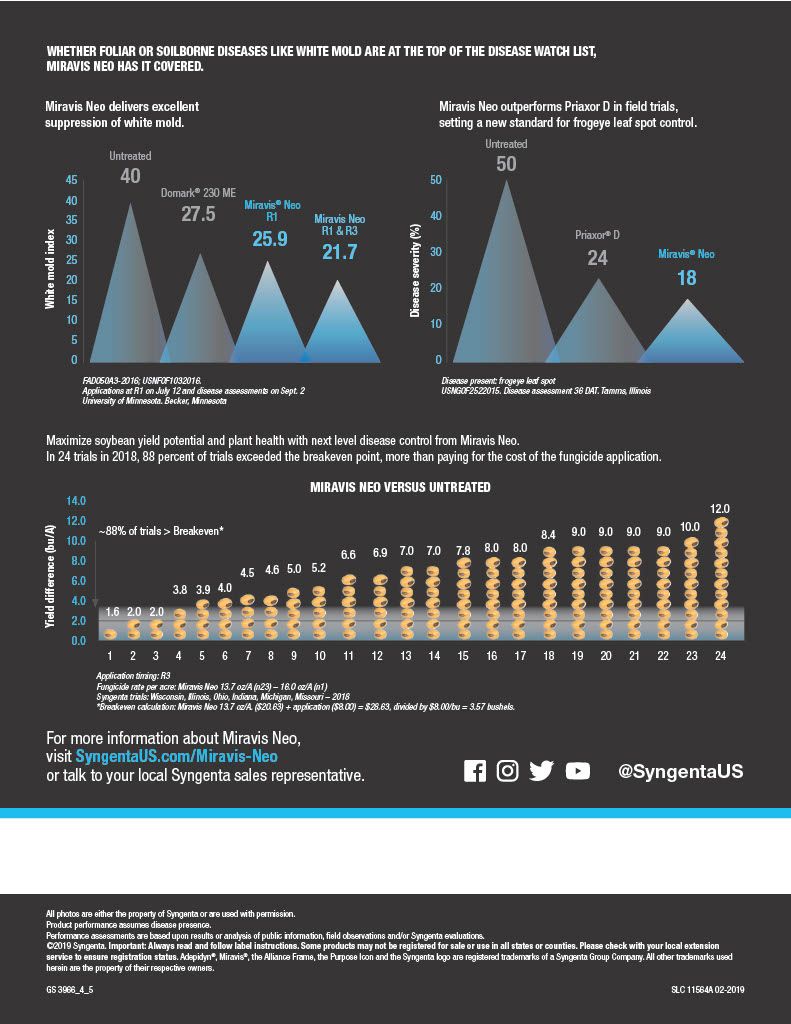
Miravis Neo is another staple of fungicide and disease resistance management, specifically designed for corn, canola, soybeans, sorghum and quinoa. It is classified as a class 3, 7 and 11 systemic fungicide for the treatment of a wide range of fungal borne diseases, including but not limited to, Anthracnose leaf blight, brown spot, common rust, curvularia leaf spot, soybean rust, eye spot, gray leaf spot, northern corn leaf blight, northern corn leaf spot, southern corn leaf blight, southern rust, tar spot, powdery mildew and many others. Miravis Neo works to limit damage done by yield reducing fungi and it has been proven in field trials to improve yield over many other competitors as shown in the attachments in the product gallery.
The contents of Miravis Neo are as follows:
Pydiflumetofen** . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.0%
Azoxystrobin*** . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.3%
Propiconazole**** . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.6%
Other Ingredients: 72.1%
Total: 100.0%
EPA Reg. No. 100-1605
Miravis Neo should be integrated into an overall disease and pest management strategy whenever the use of a fungicide
is required. Cultural practices known to reduce disease development must be followed. This must include selection of
varieties with disease tolerance, removal of plant debris in which inoculum overwinters, and proper timing and placement
of irrigation. Consult your local agricultural authorities for additional IPM strategies established for your area. Miravis Neo
may be used in State Agricultural Extension advisory (disease forecasting) programs which advise application timing
based on environmental factors favorable for disease development.
For resistance management, please note that Miravis Neo contains a Group 7 (pydiflumetofen), a Group 3 (propiconazole),
and a Group 11 (azoxystrobin) fungicide. Any fungal population may contain individuals naturally resistant to Miravis Neo
and other Group 7, Group 3, and Group 11 fungicides. A gradual or total loss of pest control may occur over time if these
fungicides are used repeatedly in the same fields. Follow appropriate resistance-management strategies.
To delay fungicide resistance, take one or more of the following steps:
• Rotate the use of Miravis Neo or other Group 7, Group 3, and Group 11 fungicides within a growing season sequence
with different groups that control the same pathogens.
• Use tank mixtures with fungicides from a different group that are equally effective on the target pest when such use is
permitted. Use at least the minimum application rate as labeled by the manufacturer.
• Adopt an integrated disease management program for fungicide use that includes scouting, uses historical information
related to pesticide use, and crop rotation, and which considers host plant resistance, impact of environmental
conditions on disease development, disease thresholds, as well as cultural, biological and other chemical control
practices.
• Where possible, make use of predictive disease models to effectively time fungicide applications. Note that using
predictive models alone is not sufficient to manage resistance.
• Monitor treated fungal populations for resistance development.
As part of a resistance management strategy:
• Apply no more than 2 sequential applications unless otherwise stated in the crop section.
• Follow the crop-specific resistance management directions in Section 7.0.
Customer reviews
Reviews only from verified customers
No reviews yet. You can buy this product and be the first to leave a review.
Miravis Neo (Syngenta)
You May Also Like
Bulk Discounts Available

Cueva (CertisBio)
Cueva (CertisBio)
Copper based fungicide that is powerful enough to combat blights, rusts and other common fungal diseases
SKU 1070
$433.99

Phosgard Bio (JH Biotech)
Phosgard Bio (JH Biotech)
Dual purpose Bio fertilizer and Fosphite fungicide
SKU 1016
$249.55
New! Lower Price for Growers

Oxidate 2.0
Oxidate 2.0
With a 0 DayPHI and 1 Hr REI, This is an effective all purpose fungicide and sanitation agent
SKU 1038
was $118.26
Save 8%
$108.50
Bulk discounts available

Trilogy
Trilogy
Organic Fungicide, Miticide & Insecticide that incorporates in your IPM system
SKU 1015
$368.90
Bulk discounts available

ZeroTol 2.0
ZeroTol 2.0
Your Greenhouse Fungicide Solution to Keep Bacterial and Fungal Diseases at Bay
SKU 1005
$113.92
Bulk Discounts Available

Miravis Prime (Syngenta)
Miravis Prime (Syngenta)
Yield enhancing broad spectrum fungicide for Fruits, Vegetables, Specialty Crops with dual modes of action
SKU 1063
$3,417.75
Buy in bulk to save $$$

Luna Fungicides
Luna Fungicides
Fungicide Options from Bayer to clear fungal diseases
SKU 1026
$705.25
Save money, buy a case or bulk

Safergro Mildew Cure
Safergro Mildew Cure
OMRI Based fungicide
SKU 1006
was $88.97
Save 15%
$75.95
Bulk discounts available

Fosphite (JH Biotech)
Fosphite (JH Biotech)
4-hour Re-Entry interval. 0-day Pre-Harvest interval. 2 modes of action: fungicide and growth promoter
SKU 1001
$325.49